Table of contents
Digital transformation is an ongoing process that is gaining momentum worldwide, including in Germany. Germany has made significant progress in digital transformation in recent years, with government and businesses alike investing in digital technologies and infrastructure.
In particular, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital technologies in Germany, as many companies and individuals have had to switch to remote work and digital communication.
The federal government has also implemented various initiatives to support digital transformation, such as the Digital Pact for Schools, a program to provide digital infrastructure in schools, and the Digital Hub Initiative, which aims to support digital startups.
However, these efforts are not sufficient in international comparison.
According to the OECD, Germany is one of the last places in terms of speed when it comes to internet infrastructure. In addition, spending is among the lowest in relation to economic power.
Bloomberg quotes from a recent OECD report: “In no other major industrialized nation has the basis of competitiveness and resilience been challenged so systematically by changing social, environmental and regulatory constraints.”
So there is a lot to do to remain internationally competitive.
Against the background of these developments, I take a look from time to time at how industries, companies, and technology providers around the world are tackling relevant issues and which initiatives are noteworthy.
With regard to Industry 4.0 and 5G, this time I explored key projects of the Chinese technology company Huawei in the areas of smart manufacturing, smart logistics, and healthcare.
Industry 4.0 and 5G are key
Industry 4.0 and 5G are two of the most important technological advances currently shaping the future of industries around the world.
A look at the numbers underlines this: The Industry 4.0 market is expected to grow from USD 130.90 billion last year to USD 377.30 billion in 2030, registering a CAGR of 16.3% over the forecast period (Source: Contrive Datum Insights and Globe Newswire).
The 5G infrastructure market, part of the 5G technology market (hardware, software, and services), is expected to grow by USD 95.89 billion from this year to 2030 (Source: Bloomberg).
Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by the integration of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing into various industries. On the other hand, 5G is the fifth-generation mobile network that offers faster internet speeds, lower latency, and higher capacity.
The combination of Industry 4.0 and 5G has the potential to revolutionize industries by enabling faster and more efficient communication between machines, facilitating real-time data analysis, and improving automation. This will result in higher productivity, lower costs, and improved quality control. In addition, the introduction of these technologies can also lead to the creation of new business models and revenue streams.
In the manufacturing industry, for example, integrating Industry 4.0 and 5G can help streamline production processes, reduce waste, and improve product quality. In healthcare, these technologies can help develop remote patient monitoring systems, robotic surgeries, and telemedicine.
Overall, the combination of Industry 4.0 and 5G has the potential to transform industries and improve the way we live and work. Companies and individuals need to stay abreast of these advances and adapt to the changing landscape to remain competitive.
Let’s dive deeper into the relevant requirements as well as specific Huawei projects manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare.
Smart manufacturing
As the leading manufacturing hub in Europe, Germany is at the forefront of this change. However, the country faces several challenges in implementing smart manufacturing.
In 2021, over 65% of German companies had adopted Industry 4.0 practices, with another 25% preparing to follow suit. According to the Global Innovation Index 2022, Germany is also the eighth most innovative country in the world.
However, the country is falling further behind in international comparison when it comes to digital transformation.

What are the core challenges in smart manufacturing?
- Lack of skilled workforce: With rapid technological advancements, the manufacturing sector requires workers with specialized skills and knowledge to operate and maintain advanced manufacturing systems. However, there is currently a shortage of such workers in Germany. To address this problem, the government is investing in education and training programs to develop a skilled workforce.
- High implementation costs: While smart manufacturing offers long-term benefits, the initial investment required can be a significant barrier to adoption. This is particularly true for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which may lack the financial resources to invest in new technologies. To make it easier for SMEs to access smart manufacturing, the government offers incentives and support programs.
- Data security: As the use of connected systems and IoT devices increases, the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches also increases. The manufacturing sector is particularly at risk because it works with sensitive information such as trade secrets and intellectual property. To mitigate this risk, the government is working to improve cybersecurity measures and promote awareness of the importance of data security.
What solutions are there for these challenges?
Despite these challenges, the federal government is committed to driving forward the introduction of Industry 4.0 technologies. To achieve this, they are launching several initiatives including:
- Investment in education and training programs: The government is investing in education and training programs to develop a skilled workforce capable of operating and maintaining advanced manufacturing systems.
- Incentives and support programs: To help SMEs access smart manufacturing, the government offers incentives and support programs that include financing, tax breaks, and low-interest loans.
- Promotion of data security: The government is working to improve cybersecurity measures and raise awareness of the importance of data security in the manufacturing sector.
When all relevant smart manufacturing factors work together optimally, factories of the future can be built that not only impress with above-average increases in efficiency but also take contemporary sustainability aspects into account.
What we can learn from Midea in Jingzhou, China
Midea’s washing machine factory in Jingzhou, Hubei Province is the world’s first fully 5G connected home appliance manufacturing plant, leveraging 5G to provide a fully connected manufacturing process.
This is the industry’s largest 5G application on industrial sites to date, with the largest number of 5G devices deployed and the most extensive use of 5G in production. The factory-wide 5G network enables end-to-end digitalization, advanced logistics, automated robotics, real-time production line monitoring, and quality inspections using artificial intelligence.
The product GTM cycle in the new factory will be shortened by more than 60 days. It takes only 15 seconds to produce a washing machine, reducing inventory by 50% and labor costs per product by 30%. At the same time, the sensors, instruments, and cameras connected to 5G help manage energy consumption, track environmental factors, increase security, and maintain site security.
Midea’s holistic use of 5G represents a complete departure from the traditional approach to connecting a factory. Due to its successful practice, the project also won the GSMA GLOMO’s “5G Industry Challenge Award” in 2023.
Smart logistics
Smart logistics is the integration of digital technologies into the supply chain to improve efficiency and reduce costs. In Germany, a highly developed and export-oriented economy, intelligent logistics presents both opportunities and challenges.
What are the core challenges in smart logistics?
One of the biggest challenges is the lack of standardization in the logistics industry. This makes it difficult to integrate new technologies and systems into existing logistics processes.
Another challenge is the high cost of implementing intelligent logistics solutions. Organizations are reluctant to invest in expensive new technologies without a clear return on investment. In addition, the logistics industry lacks skilled workers who have the necessary knowledge and expertise to implement and manage intelligent logistics solutions.

What solutions are there for these challenges?
Despite these challenges, smart logistics has the potential to significantly improve the efficiency and sustainability of the logistics industry in Germany. By using technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain, companies can optimize their supply chains and reduce waste, costs, and emissions.
A joint effort from logistics companies, technology providers, and policymakers is required to address these challenges and fully exploit the benefits of intelligent logistics in Germany.
To overcome the challenges of smart logistics in Germany, several steps can be taken:
- Standardization: The logistics industry needs to work towards standardization to ensure that new technologies and systems can be easily integrated into existing processes. This requires collaboration between logistics companies, technology providers, and policymakers to establish common standards and protocols.
- Cost-benefit analysis: Companies need to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis before investing in smart logistics solutions. This will help them identify areas where they can get the most value and prioritize their investments accordingly.
- Training and education: To address the skills shortage in the logistics industry, a concerted effort is required to train and educate the workforce in the latest technologies and systems. This can be achieved through partnerships between logistics companies and educational institutions.
- Data protection and security: When implementing intelligent logistics solutions, companies need to prioritize data protection and security. This can be achieved by conducting regular audits and assessments of data protection measures and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
- Collaboration: To fully realize the benefits of smart logistics, greater collaboration is needed between logistics companies, technology providers, and policymakers. This can be achieved through initiatives such as public-private partnerships and industry forums.
When all relevant smart logistics factors are optimally coordinated, transport networks can be built that not only reduce costs through significant operational efficiency but also reduce energy consumption.
What we can learn from East-West Gate Intermodal Terminal (EWG) in Hungary
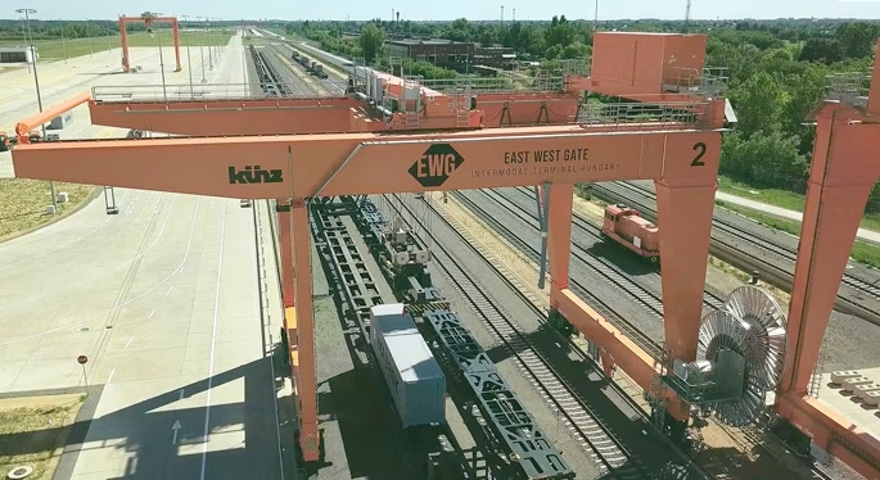

Since October 2022, the East-West Gate Intermodal Terminal (EWG) in Hungary has served as a hub for the region’s rail, road, and waterway transport networks and is now the largest intermodal rail hub in Europe.
EWG deploys Huawei’s customized, highly data-secure 5G private network, which enables real-time wireless remote control and intelligent monitoring of the entire container terminal area, significantly improving operation efficiency by over 20% and reducing costs by over 40%.
In addition to its business values, the terminal places great emphasis on the environment in its operations. The terminal is powered by renewable energy such as solar panels and has a rainwater harvesting system to reduce water consumption. The environmental and sustainability features also make it a more sustainable and responsible transport hub.

Healthcare
Digital transformation in healthcare has long been an issue in Germany and has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic. However, it is not without its challenges.
What are the core challenges in healthcare?
One of the biggest challenges is the lack of standardization of digital health systems and processes. This makes it difficult to integrate different systems and data sources and to exchange data securely between different healthcare providers.
Another challenge is the issue of data protection and security. Due to the sensitivity of health data, it must be protected from cyber threats and unauthorized access. Additionally, it is important to ensure that patient data is used ethically and transparently.
What solutions are there for these challenges?
To overcome the challenges of digital transformation in the healthcare system in Germany, stakeholders need to collaborate and implement effective solutions. Some possible solutions include:
- Standardization: Developing common standards for digital health systems and processes can facilitate data exchange and integration. This can be achieved through collaboration between healthcare providers, government, and industry stakeholders.
- Data protection and security: Implementing strong cybersecurity measures and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations can help protect sensitive health information. In addition, transparency and ethical handling of patient data should be a priority.
- Digital skills training: Providing digital skills training to healthcare professionals can improve their ability to adapt and effectively use digital health technologies. This can be achieved through partnerships between healthcare providers, educational institutions, and technology companies.
- Investment in infrastructure: Increasing investments in digital infrastructure and interoperability can enable seamless data exchange between different healthcare providers. This can be supported by government funding, private investment, and public-private partnerships.
When all relevant factors are optimally taken into account, solutions for the healthcare sector can be developed that not only reduce the total cost of ownership but also increase the quality of treatment for patients.
What we can learn from IT modernization at Essen University Hospital, Germany
With strong practices in the areas of oncology, organ transplantation, cardiology, and rare diseases, Essen University Hospital is one of the largest facilities of its kind. With 1,770 beds and 10,000 employees, around 375,000 patients are treated every year. This results in the need to manage enormous amounts of patient records, each containing large amounts of data.
Scans and test results become more detailed, increasing file size. Printed records are giving way to electronic medical records, which are easier to share. However, high-resolution images and their archiving can easily become a burden on the network, distracting IT managers’ attention and increasing costs.
Comprehensive, low-latency digital storage has become a cornerstone of good medical care. It allows primary care physicians and specialists to access complete patient records when needed. Making this a reality requires consolidating data running on disparate systems, upgrading legacy devices, and establishing low-latency communications networks and data storage systems.
At Essen University Hospital, Huawei deployed low-latency all-flash storage systems powered by proprietary network chipsets. Huawei also oversaw the transition from the old to the new system. The new storage infrastructure provides extremely stable network performance and can easily handle rapid data growth. Network latency is now just 0.3 milliseconds.
High-performance storage systems open up new ways of treating patients. Rapid access to large amounts of data enables the development and training of medical AI tools that diagnose patients faster and more accurately. Rapid access to data also enables the use of AI to develop new treatments for rare diseases. Additionally, smart storage facilitates remote patient care by making it easier to access and share data from different locations.
The project achieved significant savings. The hospital estimates that the acquisition cost was 30% lower than comparable equipment from other vendors and the total cost of ownership was reduced by 50%.
Conclusion
Overall, there are certainly challenges associated with digital transformation in Germany, but there are also promising opportunities for companies that are willing to invest in the necessary skills and technologies to drive change. By addressing these challenges, organizations can position themselves for success in the digital age.
There are numerous ways to do this. Among other things, companies can collaborate with partners in the digital ecosystem to leverage their expertise and accelerate the pace of digital transformation. This may include working with technology providers to test new digital solutions or working with technology providers to implement off-the-shelf solutions.
Based on successfully implemented projects, innovative strength, and a comprehensive international partner network, Huawei has the prerequisites to advance the key topics of Industry 4.0 and 5G.

